ReSTIR GI 공부 노트 (2022.04.21)
ReSTIR 논문 요약
배경
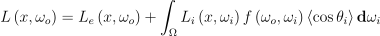
결국 위의 방정식 구하자고 하는 짓임.
결국 아래 그림처럼 되는 것임:
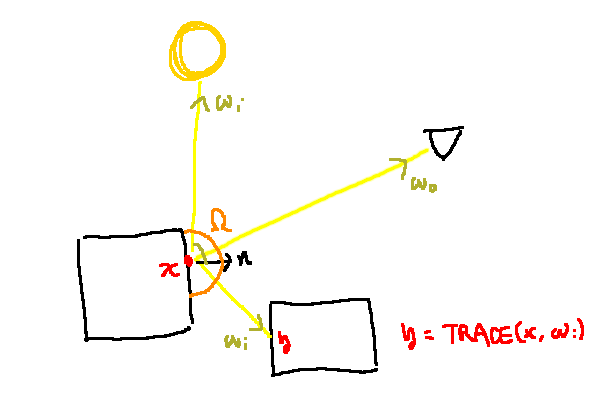
여기서 f는 BSDF.
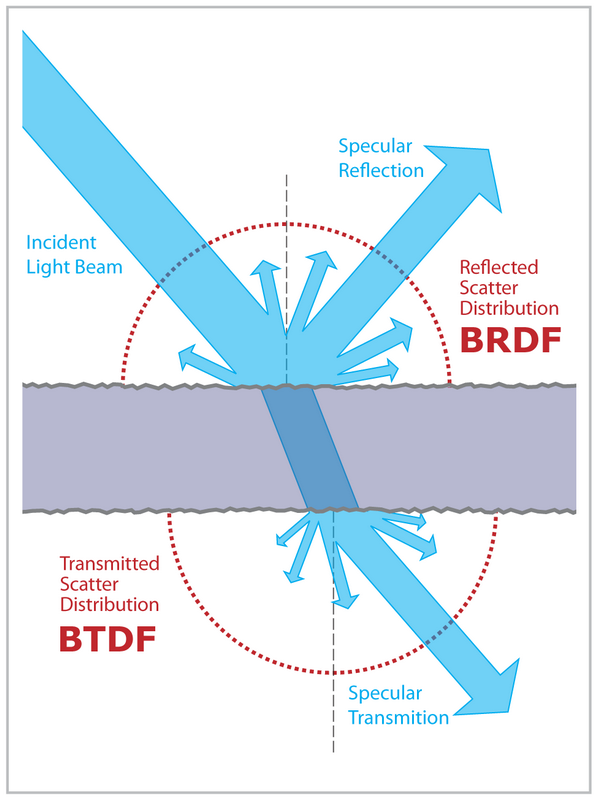
BRDF, BTDF, BSDF
By Jurohi (talk) (Uploads) - Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0, Link
- Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function
- Bidirectional Transmittance Distribution Function
- Bidirectional Scattering Distribution Function
BRDF는 “이 표면 위의 한 점에 ωi의 방향으로 빛이 들어왔을 때, ωo의 방향으로 빛이 반사될 확률이 얼마일까요?라는 의미.
BTDF는 “이 표면 위의 한 점에 ωi의 방향으로 빛이 들어왔을 때, ωo의 방향으로 빛이 투과할 확률이 얼마일까요?
BSDF는 “이 표면 위의 한 점에 ωi의 방향으로 빛이 들어왔을 때, ωo의 방향으로 빛이 산란할 확률이 얼마일까요?
위의 예시 그림에서 Li 곧바로 광원에서 오는 빛이지만, 사실 광원이 아닌 곳에서 들어오는 간접광일 수도 있음:

Li는 들어오는 빛이고, Lo는 나가는 빛.
즉, x로 들어오는 입사광 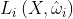 은 결국 해당 경로를 추적했을 때 가장 가까운 지점 y, 즉 TRACE(x, ωi)에서 x 방향으로 나가는 빛, 즉 Lo(y, x - y) = Lo(TRACE(x, ωi), -ωi)임.
은 결국 해당 경로를 추적했을 때 가장 가까운 지점 y, 즉 TRACE(x, ωi)에서 x 방향으로 나가는 빛, 즉 Lo(y, x - y) = Lo(TRACE(x, ωi), -ωi)임.
여튼 결론적으로 x 지점에서 카메라로 오는 빛을 구하는게 핵심인데, x 지점에서의 빛은 결국 Ω라는 반구 방향으로 오는 빛들을 전부 합한 것임.
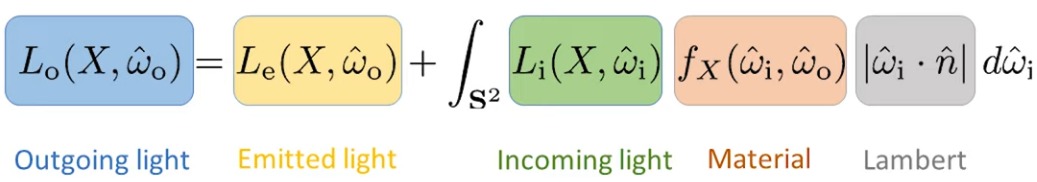
근데 이게 컴퓨터에서 사실 적분을 하라는 건 컴퓨터보고 죽으라는 소리임.

그럼 이걸 도대체 어떻게 구하라는걸까?
사실 이건 간단하다. 민주주의 체제를 생각하면 된다. 민주주의 체제에서 뭔가 국가적인 판단을 하려면 사실 모든 국민에게 물어보면 된다. 모든 국민이 투표를 하면 끝이지만, 이게 실질적으로 불가능하다. 그러니 행정부, 입법부, 사법부라는 것이 국민을 대표하여 존재하는 것.
이처럼 빛도 대표자를 뽑으면 된다.
이걸 해주는 것이 바로 몬테 카를로 방법.
대표자를 뽑기 위해 좋은 확률 분포 함수 p(ωj)를 사용해주는 것. 확률 분포 함수가 피적분 함수와 비슷할 수록 몬테 카를로 추정치의 오류가 당연히 줄어들 것임.
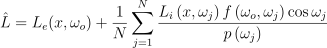
아무나 대표로 뽑으면 나라가 지옥으로 향하는 고속도로 하이패스 끊듯이, 빛도 마찬가지다. x로 들어오는 빛도 좋은 친구를 뽑아야 한다. 이럴 때 사용하는 대표적인 방법이 중요도 표집의 재표집(Resampled Importance Sampling. RIS). 이름부터 한 번 표집했던 표본들을 다시 사용해먹겠단 소리니까 우선 p(y)에 따라 M 개의 표본을 y를 표집함. 그 다음엔 “목표 확률 분포 함수”  에 따라 y의 한 표본 z를 재표집함:
에 따라 y의 한 표본 z를 재표집함:
이때
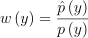
임.
즉, 재표집 확률 / 초기 표본을 구하는 확률이므로, 상대적인 가중치라 볼 수 있음.
ReSTIR 구현
RTXDI
Script
- VBufferRT [out: vbuffer, mvec]
- RTXDIPass [in: vbuffer, mvec], [out: color]
- AccumulatePass [in: input], [out: output]
- ToneMapper [in: src], [out: dst]
RTXDIPass
RTXDIPass::reflect
- Input Channels:
- visibility buffer in packed format
- texture gradients (optional)
- motion vector buffer (float format) (optional)
- Output Channel
- final color
- emissive color
- diffuse illumination
- diffuse reflectance
- specular illumination
- specular reflectance
RTXDIPass::execute
- Update refresh flag if changes that affect the output have occured
- Check if GBuffer has adjusted shading normals enabled
- RTXDI begin frame
- Prepare surface data
- RTXDI update
- Final shading
- RTXDI end frame
RTXDI
RTXDI::beginFrame
- Called by
- Load shaders if required
- Create RTXDI context and allocate resources if required
- Clear reservoir buffer if requested
- Determine what, if anything happened since last frame
- Pixel Debug begin frame
RTXDI::loadShaders
- Called by
- Create compute pass
ReflectTypes.cs.slang - Issue warnings if packed types are not aligned to 16B for best performance
- Helper for creating compute passes
- Load compute passes for setting up RTXDI light information
- Create update lights compute pass
LightUpdater.cs.slang - Create update environment light compute pass
EnvLightUpdater.cs.slang
- Create update lights compute pass
- Load compute passes for RTXDI sampling and resampling
- Create presample local lights compute pass
RTXDISetup.cs.slangpresampleLocalLights - Create presample environment light compute pass
RTXDISetup.cs.slang,presampleEnvLight - Create generate candidates compute pass
RTXDISetup.cs.slang,generateCandidates - Create test candidate visibility compute pass
RTXDISetup.cs.slang,testCandidateVisibility - Create spatial resampling compute pass
RTXDISetup.cs.slang,spatialResampling - Create temporal resampling compute pass
RTXDISetup.cs.slang,temporalResampling - Create spatiotemporal resampling compute pass
RTXDISetup.cs.slang,spatiotemporalResampling
- Create presample local lights compute pass
RTXDI::prepareResources
- Called by
- Ask for some other refreshes elsewhere to make sure we’re all consistent
- Make sure the RTXDI context has the current screen resolution
- Set the number and size of our presampled tiles
- Create a new RTXDI context
- Additional resources are allocated lazily in updateLights() and updateEnvMap()
- Allocate buffer for presampled light tiles (RTXDI calls this “RIS buffers”)
- Allocate buffer for compact light info used to improve coherence for presampled light tiles
- Allocate buffer for light reservoirs. There are multiple reservoirs (specified by kMaxReservoirs) concatenated together
- Allocate buffer for surface data for current and previous frames
- Allocate buffer for neighbor offsets
RTXDI::update
- Called by
- Create a PDF texture for our primitive lights (for now, just triangles)
- Update lights
- Update environment lights
- Update our parameters for the current frame and pass them into our GPU structure
- Set RTXDI frame parameters
- Create tiles of presampled lights once per frame to improve per-pixel memory coherence
- Presample lights
- Reservoir buffer containing reservoirs after sampling/resampling
- Generate candidates
- Test candidate visibility
- Spatial / temporal resampling
RTXDI::spatialResamplingRTXDI::temporalResamplingRTXDI::spatiotemporalResampling
RTXDI::updateLights
- Called by:
- Update our list of analytic lights to use (except analytic area lights)
- Update light counts
- Update list of light IDs, local lights followed by infinite lights
- Create GPU buffer for holding light IDs
- Update GPU buffer
- Update other light counts
- Allocate buffer for light infos
- Allocate local light PDF texture, which RTXDI uses for importance sampling
- If the layout of local lights has changed, we need to make sure to remove any extra non-zero entries in the local light PDF texture. We simply clear the texture and populate it from scratch
- If the number of emissive lights has changed, we need to update the analytic lights because they change position in the light info buffer
- Run the update pass if any lights have changed
- Compute launch dimensions
- Execute update lights pass
LightUpdater.cs.slang
- Execute update lights pass
- Compute launch dimensions
- Update the light PDF texture mipmap chain if necessary
- Keep track of the number of local lights for the next frame
RTXDI::updateEnvLight
- Called by:
- If scene uses an environment light, create a luminance & pdf texture for sampling it
- RTXDI expects power-of-two textures
- Create luminance texture if it doesn’t exist yet or has the wrong dimensions
- Create pdf texture if it doesn’t exist yet or has the wrong dimensions
- Update env light textures
- execute update environment light pass
EnvLightUpdater.cs.slang
- execute update environment light pass
- Create a mipmap chain for pdf texure
RTXDI::setRTXDIFrameParameters
- Called by
- Set current frame index
- Always enable importance sampling for local lights
- Set the range of local lights
- Set the range of infinite lights
- Set the environment light
- In case we’re using ReGIR, update the grid center to be at the camera
- Update the parameters RTXDI needs when we call its functions in our shaders
RTXDI::endFrame
- Called by
RTXDI::presampleLights
- Called by
- Presample local lights
RTXDI::setShaderDataInternal- Execute presample local lights pass
RTXDISetup.cs.slang,presampleLocalLights
- Presample environment light
RTXDI::setShaderDataInternal- Execute presample environment light pass
RTXDISetup.cs.slang,presampleEnvLight
RTXDI::setShaderDataInternal
- Send our parameter structure down
- Parameters needed inside the core RTXDI application bridge
- Parameters for initial candidate samples
- Parameters for general sample reuse
- Parameter for final shading
- Parameters for generally spatial sample reuse
- Parameters for last frame’s camera coordinate
- Setup textures and other buffers needed by the RTXDI bridge
- PDF textures for importance sampling. Some shaders need UAVs, some SRVs
RTXDI::generateCandidates
- Called by
RTXDI::setShaderDataInternal- Execute Generate candidates pass
RTXDISetup.cs.slang,generateCandidates
RTXDI::testCandidateVisibility
- Called by
RTXDI::setShaderDataInternal- Execute test candidate visibility pass
RTXDISetup.cs.slang,testCandidateVisibility
RTXDI::spatialResampling
- Called by
RTXDI::setShaderDataInternal- Execute spatial resampling pass
RTXDISetup.cs.slang,spatialResampling
rtxdi::Context
rtxdi::Context::GetRisBufferElementCount
- Called by
rtxdi::Context::GetReGIRLightSlotCount
rtxdi::Context::GetReGIRLightSlotCount
- Called by
- Returns number of light slots by given ReGIR Mode
rtxdi::Context::GetReservoirBufferElementCount
- Called by
rtxdi::Context::FillNeighborOffsetBuffer
- Called by
- Create a sequence of low-discrepancy samples within a unit radius around the origin for “randomly” sampling neighbors during spatial resampling
rtxdi::ComputePdfTextureSize
- Called by
- Compute the size of a power-of-2 rectangle that fits all items, 1 item per pixel
rtxdi::Context::FillRuntimeParameters
- Called by
LightUpdater.cs.slang
LightUpdater::execute
- Executed by:
Update the light info and local light PDF texture
- If light index is lower than the first local analytic light
- Create emissive lights
- Get the scene triangle index of the emissive light
- Load emissive triangle data
- Setup emissive light
- Create emissive lights
- Else if light index is lower than the environment light index
- Create analytic lights
- Get the index of the light in the scene
- Setup analytic light
- Create analytic lights
- Else (if light index equals the environment light index)
- Create environment light
EnvLightUpdater.cs.slang
EnvLightUpdater::execute
- Executed by:
- Compute UV coordinates in env map
- Evaluate the env map luminance
- Write luminance
- Compute relative solid angle to account for compression at the poles
- Write PDF
RTXDI.slang
RTXDI::presampleLocalLights
- Executed by:
Presample local lights into presampled light tiles
- Initialize random sampler
- Presample local lights
RTXDI::presampleEnvLight
- Executed by:
Presample environment light into presampled light tiles
RTXDI::generateCandidates
- Executed by:
- Initialize random samplers
- Load surface data
- Generate initial candidates
- Store selected light sample in a reservoir for later reuse and shading
RTXDI::testCandidateVisibility
- Executed by:
Trace a visibility ray from the primary hit surface to the light sample in the reservoir. Update the reservoir if the light is not visible.
- Load surface data and reservoir containing the light sample
- Get the light sample, so we have data to construct our visibility query
- Trace a visibility ray and update the reservoir
RTXDI::doSpatialResampling
- Executed by:
Perform spatial resampling
- Initialize random sampler
- Load surface data
- Load reservoir at the current pixel
- Setup resampling parameters
- Execute resampling
ResamplingFunctions.hlsli
RTXDI_PresampleLocalLights
- Executed by:
- Sample PDF Mipmap
- Store the index of the light that we found and its inverse pdf. Or zero and zero if we somehow found nothing
RTXDI_SamplePdfMipmap
- Executed by:
RTXDI_InitSampleParameters
- Executed by:
- Sample parameters struct
- Defined so that so these can be compile time constants as defined by the user
- brdfCutoff Value in range [0, 1] to determine how much to shorten BRDF rays. 0 to disable shortening
RTXDI_SampleLightsForSurface
- Executed by:
Samples ReGIR and the local and infinite light pools for a given surface
- Local lights
- If ReGIR is enabled and the surface is inside the grid, sample the grid. Otherwise, fall back to source pool sampling.
- Infinite lights
- Environment map
- BRDF
- Combine reservoirs
- Finalize resampling
RTXDI_SampleLocalLightsFromReGIR
- Executed by:
Sampling lights for a surface from the ReGIR structure or the local light pool.
If the surface is inside the ReGIR structure, and ReGIR is enabled, and numRegirSamples is nonzero, then this function will sample the ReGIR structure.
Otherwise, it samples the local light pool.
RTXDI_SampleLocalLights
- Executed by:
Samples the local light pool for the given surface
RTXDI_SampleInfiniteLights
- Executed by:
Samples the infinite light pool for the given surface
RTXDI_SampleEnvironmentMap
- Executed by:
RTXDI_SampleBrdf
- Executed by:
RTXDI_CombineReservoirs
- Executed by:
Adds newReservoir into reservoir, returns true if the new reservoir’s sample was selected.
Algorithm (4) from the ReSTIR paper, Combining the streams of multiple reservoirs.
Normalization - Equation (6) - is postponed until all reservoirs are combined.
RTXDI_FinalizeResampling
- Executed by:
Performs normalization of the reservoir after streaming. Equation (6) from the ReSTIR paper.
RTXDI_StoreReservoir
- Called by:
RTXDI_PresampleEnvironmentMap
- Called by:
- Uniform sampling inside the pixels
- Convert texel positions to UV and pack it
- Compute the inverse PDF if we found something
- Store the result
RTXDI_SpatialResampling
- Called by:
Spatial resampling pass Operates on the current frame G-buffer and its reservoirs
ReSTIR GI 구현
Kajiya
Pass
rtdgi
rtdgi temporal//shaders/rtdgi/temporal_filter2.hlslrtdgi spatial2//shaders/rtdgi/spatial_filter2.hlslrtdgi reproject//shaders/rtdgi/fullres_reproject.hlslrtdgi trace/shaders/rtdgi/trace_diffuse.rgen.hlsl/shaders/rt/gbuffer.rmiss.hlsl/shaders/rt/shadow.rmiss.hlsl/shaders/rt/gbuffer.rchit.hlsl
validity integrate//shaders/rtdgi/temporal_validity_integrate.hlslrestir temporal//shaders/rtdgi/restir_temporal.hlsl- Reads:
- Half view normal (from GBuffer)
- GBuffer depth
- Candidate irradiance (from RTDGI)
- Candidate normal
- Irradiance history
- Ray origin history
- Ray history
- Reservoir history
- Reprojection map
- Hit normal history
- Candidate history
- Validity
- Writes:
- Irradiance
- Ray origin
- Ray
- Hit normal
- Reservoir
- Candidate
- Reads:
restir spatial//shaders/rtdgi/restir_spatial.hlsl- Reads:
- Irradiance
- Hit normal
- Ray
- Reservoir
- GBuffer depth
- Half view normal
- Half depth
- SSAO
- Candidate
- Writes:
- Reservoir
- Reads:
restir resolve//shaders/rtdgi/restir_resolve.hlsl- Reads:
- Irradiance
- Hit normal
- Ray
- Reservoir
- GBuffer depth
- Half view normal
- Half depth
- SSAO
- Candidate irradiance
- Candidate normal
- Writes:
- Irradiance output
- Reads:
Falcor
ReSTIR GI 관련 블로그 글
정반사용 ReSTIR GI
다중튕김 전역조명에서 제일 중요한 건 “어느 방향”으로 광선을 쏠 건지임. 실시간에선 광선을 여러 개 못 쓰니까 광선 하나 하나가 의미가 있어야 함.
이 글에서는 특히나 정반사 환경에서 의미 있는 광선을 표집하는 법에 대해 논함.
기본 개념: ReSTIR GI1. 서브 개념: RIS2, ReSTIR3.
 Ground truth (10k SPP)
Ground truth (10k SPP)
- 문 위에 밝은 램프 두 개.
- 바닥에 반사된 빛에서 나오는 간접광 덕분에 건물의 앞부분을 볼 수 있음.
경로 추적법을 사용하면 광선이 어디로 튈지를 결정해야함. 보통은 정반사인지, 난반사인지를 확인하고, 이 BRDF에 따라 중요도 표집하여 광선을 쏨. 그럼 또 이 새로 생성한 광선에 대해서 또 똑같은 일을 해줌. 그렇게 계속 광선을 새로 만들다보면 언젠가는 광원에 충돌하거나, 적당한 시기에 종료하고, 다시 시작할 것임.
일단 여기선 난반사만 고려하도록 함:
그 결과:
 경로 추적 BRDF 표집 (1 SPP)
경로 추적 BRDF 표집 (1 SPP)
별로임. 이거 개선하려면 다음 이벤트 추정(NEE)를 사용하면 개선 가능. 즉, 튕길 때마다 빛이 어디있는지를 찾아 빛의 기여도를 구한 다음, 그 기여도를 다시 경로를 되돌아가면서 반영해주는 것임:
 1회 튕김 BRDF 표집 + NEE (1 SPP)
1회 튕김 BRDF 표집 + NEE (1 SPP)
훨씬 나아짐. 근데 문제가 이게 난반사다보니까 사실상 모든 방향으로 광선이 튕기게 됨. 그러다보니 빛이 그리 많이 들어오진 않음. 만약 성공적으로 지금 빛을 받고 있는 땅바닥에 광선이 갔다고 쳐도, 그 다음 프레임에는 또 딴데 가있을 거임. 그러니까 한 번 써준 걸 재사용해주는게 더 나을거고, 더 나아가서 주변 픽셀들이랑 쓰까 묵을 수 있게 해주면 좋을 것임. 그렇기 때문에 ReSTIR3이 좋은 것임.
근데 원래 ReSTIR처럼 빛을 표집해서 저장해두는게 아니라, 경로를 저장해둘거임.
- 람베르트 난반사 BRDF에서 표집을 해서 방향 하나 겟
- 이 방향으로 광선 쏨
- 이 광선이 충돌한 표면에서 나오는 방사 휘도를 구함
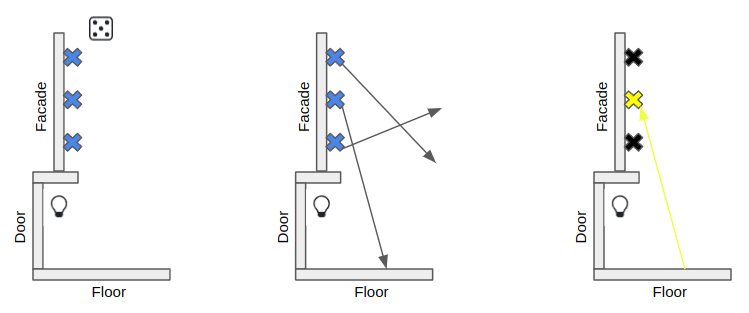 ReSTIR GI 표본 생성하는 법
ReSTIR GI 표본 생성하는 법
이게 끝임. 여기서 추가적으로 해줘야되는건 경로에 알맞고, 저장하고 읽기 적당한 RIS 가중치를 구하는 것:
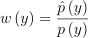
RIS 가중치
여기서 p(y)는 BRDF에서 표집(균일 표집이든… 코사인 가중치 표집이든…)하는 것에 대한 PDF로 써주면 됨.
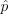 는:
는:
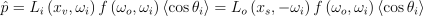
즉
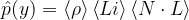
여기서 ρ를 BRDF라 치면, Li는 표본으로부터 들어오는 방사 휘도(우리가 충돌한 표면에서 떠날 때 Lo라 부름), N은 법선, L은 방향 벡터 표본.
여튼 표본이 있으니, 이걸 저장소에 저장해서 ReSTIR로 시간적으로, 공간적으로 재사용해서 개꿀빨면 됨.
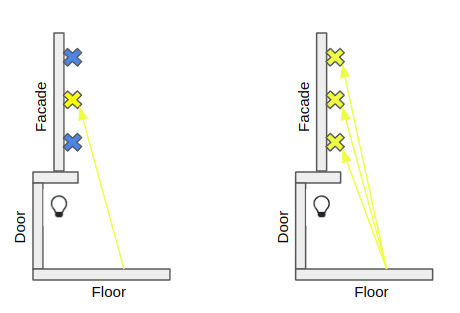 ReSTIR GI 시공간 재표집.
ReSTIR GI 시공간 재표집.
결과:
 1회 튕김 ReSTIR GI + NEE (1 SPP)
1회 튕김 ReSTIR GI + NEE (1 SPP)
픽셀들이 바닥으로 광선을 보내야한다는 걸 알기라도 하는 듯. 근데 공간 재사용할 때 주의해야하는데, 야코비 판별식으로 기하 차이를 사용해야함. 이건 논문의 4.3절에 잘 설명되어있음.
지금까지는 난반사만 다뤘는데, 사실 정반사를 사용해줘도 문제 없음. 뭐 시점만 바뀔 뿐이지 저장소, 가중치, 경로 다 똑같음.
근데 정반사, 특히나 반사율이 그리 날카롭지 않은 거친 금속 표면 등에서는 ReSTIR GI가 더 성능이 좋아짐:
 표면의 거친 정도가 서로 다른 금으로 된 기둥. (10k SPP)
표면의 거친 정도가 서로 다른 금으로 된 기둥. (10k SPP)
위의 그림에서 거친 정도는 서로 다름(20%, 40%, 60%, 80%, 100%). 광원은 지금 카메라 뒤쪽에 있고, 벽의 일부에 의해 가려져있으므로, 나머지 기둥들은 간접광을 받을 것임.
여기에 아까처럼 BRDF 표집 + NEE:
 1회 튕김 BRDF 표집 + NEE (1 SPP)
1회 튕김 BRDF 표집 + NEE (1 SPP)
막 그렇게 좋은 결과는 아님. 그렇다고 위에서처럼 바로 ReSTIR GI를 적용해줄 수 있는 것은 아님. 왜냐면 시야 벡터까지 고려해줘야함. 만약 한 방향으로 계속 빛이 들어오고 있을 때 고개를 돌리기만 해도 이게 확 변할 수도 있음. 심지어 0이 될 수도 있음. RIS 가중치를 좀 수정해야함:
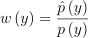
여기서 그냥 아까처럼 p(y)는 표집할 정반사 BRDF에 대한 PDF, 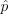 는 똑같이
는 똑같이 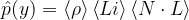 으로 해줘도 둘 다 결국 시야에 의해 달라지는 값들임. 고개 조금 까딱 돌렸는데 시간적 저장소에 대한 가중치 싹 다 다시 계산하고 그래야함? 아니면 걍 전부 0으로 만들고 다시 계산? 그럴거면 ReSTIR 왜 함? 그럼 또 야코비안 등판해야됨?
으로 해줘도 둘 다 결국 시야에 의해 달라지는 값들임. 고개 조금 까딱 돌렸는데 시간적 저장소에 대한 가중치 싹 다 다시 계산하고 그래야함? 아니면 걍 전부 0으로 만들고 다시 계산? 그럴거면 ReSTIR 왜 함? 그럼 또 야코비안 등판해야됨?
 정반사와 시야의 관계
정반사와 시야의 관계
벌써부터 시야 벡터 때문에 화가 나지만, 이걸 수학적으로 어캐 하든, 어캐 대~충 해야함.
여기선 대~충하는 방법 사용할 것임.
RIS의 특징 중 하나는 반복적으로 사용할 수 있다는 점임4. 즉, 적당히 최적인 p(y)로 표집을 해서 적당한 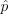 을 구하고, 이걸로 더 나은 PDF를 또 구하고… 이렇게 반복해나가는 것임.
을 구하고, 이걸로 더 나은 PDF를 또 구하고… 이렇게 반복해나가는 것임. 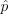 에다가 값싼 함수를 써줄 수도 있음. GGX 대신 퐁이라든가… 결국 시야 벡터 때문에 이러는 것.
에다가 값싼 함수를 써줄 수도 있음. GGX 대신 퐁이라든가… 결국 시야 벡터 때문에 이러는 것.
여튼 대충 나름? 최?적?인 p(y)를 구하는 것부터 시작하면 됨. 즉, 시야 벡터가 바뀌어도 그 값이 그대로인 PDF를 구해야함. 이거, “균일표집”이네요. 즉, 표본이 정반사 방향에 있기만 하면 시야 벡터가 바뀌어도 됨. 이 아이디어는 여기서5 온거임.
@startuml
RenderPass <|-- RayTracedGBufferPass
class RayTracedGBufferPass {
+{static} create(): SharedPtr
+~RayTracedGBufferPass()
#RayTracedGBufferPass()
#initialize(RenderContext*, ResourceManager::SharedPtr): bool
#execute(RenderContext*)
#initScene(RenderContext*, Scene::SharedPtr)
#requiresScene(): bool
#usesRayTracing(): bool
#mpRays: RayLaunch::SharedPtr
#mpScene: RtScene::SharedPtr
#mBgColor: vec3
#mFrameCount: uint32_t
}
@enduml
@startuml
RenderPass <|-- GBufferBase
enum GBufferBase::SamplePattern {
Center
DirectX
Halton
Stratified
}
class GBufferBase {
+renderUI(Gui::Widgets&)
+execute(RenderContext*, const RenderData&)
+getScriptingDictionary(): Dictionary
+setScene(RenderContext*, const Scene::SharedPtr&)
#GBufferBase(const Info&)
#parseDictionary(const Dictionary&)
#setCullMode(RasterizerState::CullMode mode)
#updateFrameDim(const uint2)
#updateSamplePattern()
#getOutput(const RenderData&, const std::string&): Texture::SharedPtr
#mpScene: Scene::SharedPtr
#mpSampleGenerator: CPUSampleGenerator::SharedPtr
#mFrameCount: uint32_t
#mFrameDim: uint2
#mInvFrameDim: float2
#mVBufferFormat: ResourceFormat
#mOutputSizeSelection: RenderPassHelpers::IOSize
#mFixedOutputSize: uint2
#mSamplePattern: SamplePattern
#mSampleCount: uint32_t
#mUseAlphaTest: bool
#mAdjustShadingNormals: bool
#mForceCullMode: bool
#mCullMode: RasterizerState::CullMode
#mOptionsChanged: bool
#{static} registerBindings(pybind11::module&)
#friend getPasses(Falcor::RenderPassLibrary&)
}
@enduml
@startuml
GBufferBase <|-- GBufferRT
class GBufferRT::struct {
+pProgram: RtProgram::SharedPtr
+pVars: RtProgramVars::SharedPtr
}
class GBufferRT {
+{static} kInfo: const Info
+{static} create(RenderContext*, const Dictionary&): SharedPtr
+reflect(const CompileData&): RenderPassReflection
+execute(RenderContext*, const RenderData&)
+renderUI(Gui::Widgets&)
+getScriptingDictionary(): Dictionary
+setScene(RenderContext*, const Scene::SharedPtr&)
-executeRaytrace(RenderContext*, const RenderData&)
-executeCompute(RenderContext*, const RenderData&)
-getShaderDefines(const RenderData&) Program::DefineList
-setShaderData(const ShaderVar&, const RenderData&)
-recreatePrograms()
-GBufferRT(const Dictionary&)
-parseDictionary(const Dictionary&)
-mComputeDOF: bool
-mpSampleGenerator: SampleGenerator::SharedPtr
-mLODMode: TexLODMode
-mUseTraceRayInline: bool
-mUseDOF: bool
-mRaytrace: struct
-mpComputePass: ComputePass::SharedPtr
}
@enduml
@startuml
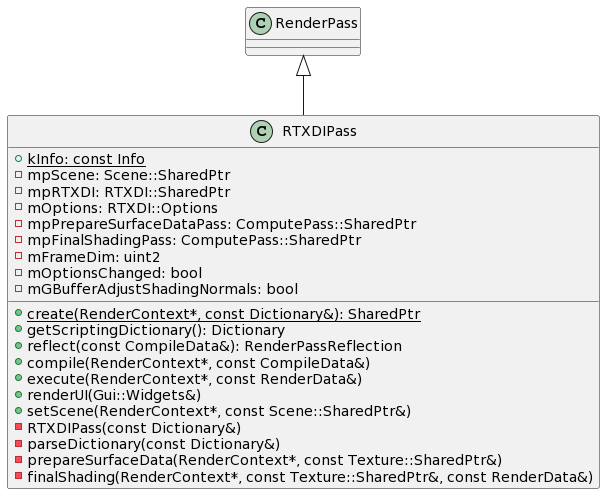
RenderPass <|-- RTXDIPass
class RTXDIPass {
+{static} kInfo: const Info
+{static} create(RenderContext*, const Dictionary&): SharedPtr
+getScriptingDictionary(): Dictionary
+reflect(const CompileData&): RenderPassReflection
+compile(RenderContext*, const CompileData&)
+execute(RenderContext*, const RenderData&)
+renderUI(Gui::Widgets&)
+setScene(RenderContext*, const Scene::SharedPtr&)
-RTXDIPass(const Dictionary&)
-parseDictionary(const Dictionary&)
-prepareSurfaceData(RenderContext*, const Texture::SharedPtr&)
-finalShading(RenderContext*, const Texture::SharedPtr&, const RenderData&)
-mpScene: Scene::SharedPtr
-mpRTXDI: RTXDI::SharedPtr
-mOptions: RTXDI::Options
-mpPrepareSurfaceDataPass: ComputePass::SharedPtr
-mpFinalShadingPass: ComputePass::SharedPtr
-mFrameDim: uint2
-mOptionsChanged: bool
-mGBufferAdjustShadingNormals: bool
}
@enduml
@startuml
enum RTXDI::Mode {
NoResampling
SpatialResampling
TemporalResampling
SpatiotemporalResampling
}
enum RTXDI::BiasCorrection
{
Off
Basic
Pairwise
RayTraced
}
class RTXDI::Options
{
+mode: Mode
+presampledTileCount: uint32_t
+presampledTileSize: uint32_t
+storeCompactLightInfo: bool
+localLightCandidateCount: uint32_t
+infiniteLightCandidateCount: uint32_t
+envLightCandidateCount: uint32_t
+brdfCandidateCount: uint32_t
+brdfCutoff: float
+testCandidateVisibility: bool
+BiasCorrection biasCorrection
+depthThreshold: float
+normalThreshold: float
+samplingRadius: float
+spatialSampleCount: uint32_t
+spatialIterations: uint32_t
+maxHistoryLength: uint32_t
+boilingFilterStrength: float
+rayEpsilon: float
+enableVisibilityShortcut: bool
+enablePermutationSampling: bool
}
class RTXDI::Light
{
+emissiveLightCount: uint32_t
+localAnalyticLightCount: uint32_t
+infiniteAnalyticLightCount: uint32_t
+bool envLightPresent
+prevEmissiveLightCount: uint32_t
+prevLocalAnalyticLightCount: uint32_t
+std::vector<uint32_t> analyticLightIDs
+getLocalLightCount(): uint32_t
+getInfiniteLightCount(): uint32_t
+getTotalLightCount(): uint32_t
+getFirstLocalLightIndex(): uint32_t
+getFirstInfiniteLightIndex(): uint32_t
+getEnvLightIndex(): uint32_t
}
class RTXDI::Flag
{
+updateEmissiveLights: bool
+updateEmissiveLightsFlux: bool
+updateAnalyticLights: bool
+updateAnalyticLightsFlux: bool
+updateEnvLight: bool
+recompileShaders: bool
+clearReservoirs: bool
}
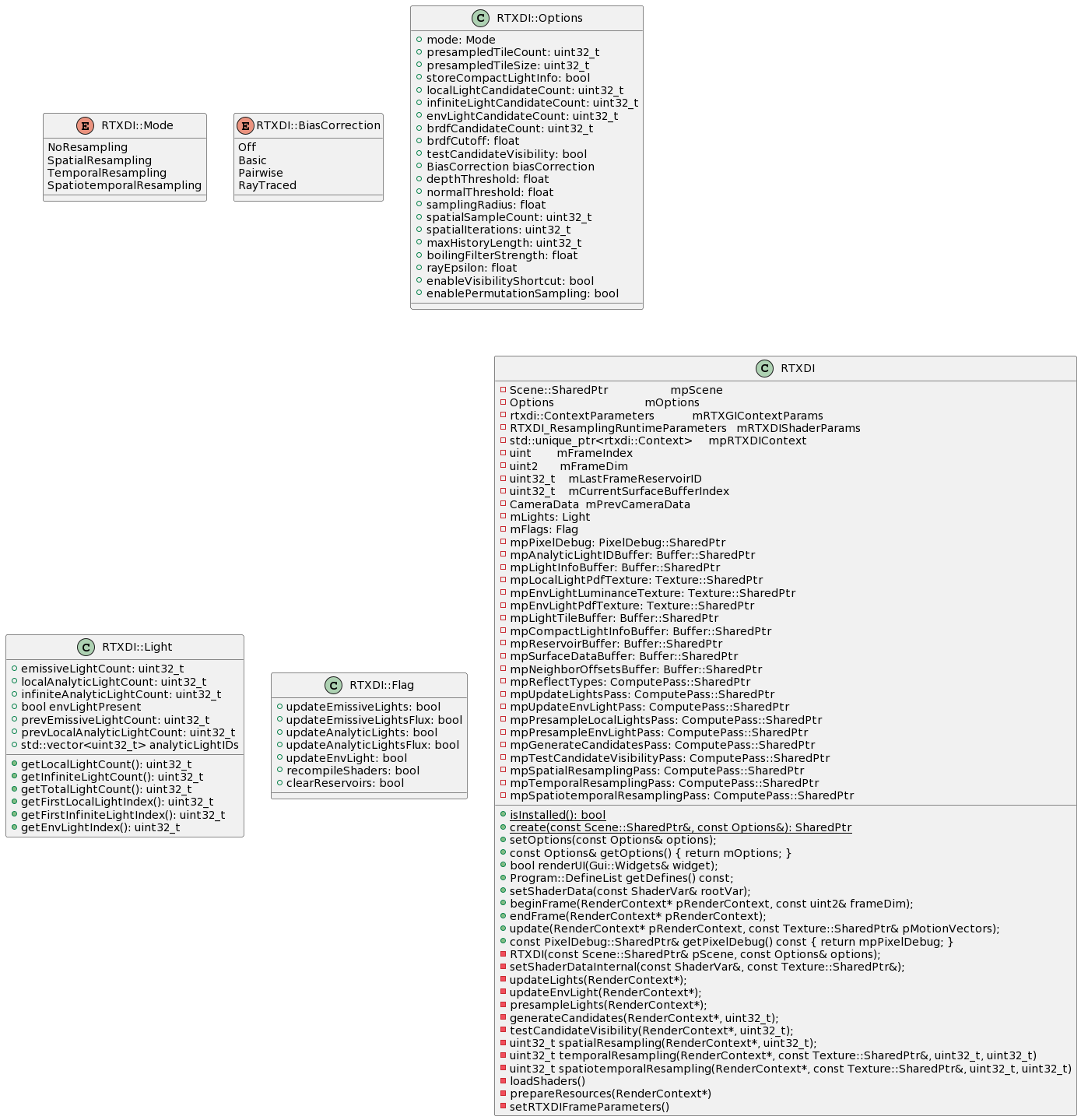
class RTXDI
{
+{static} isInstalled(): bool
+{static} create(const Scene::SharedPtr&, const Options&): SharedPtr
+setOptions(const Options& options);
+const Options& getOptions() { return mOptions; }
+bool renderUI(Gui::Widgets& widget);
+Program::DefineList getDefines() const;
+setShaderData(const ShaderVar& rootVar);
+beginFrame(RenderContext* pRenderContext, const uint2& frameDim);
+endFrame(RenderContext* pRenderContext);
+update(RenderContext* pRenderContext, const Texture::SharedPtr& pMotionVectors);
+const PixelDebug::SharedPtr& getPixelDebug() const { return mpPixelDebug; }
-RTXDI(const Scene::SharedPtr& pScene, const Options& options);
-Scene::SharedPtr mpScene
-Options mOptions
-rtxdi::ContextParameters mRTXGIContextParams
-RTXDI_ResamplingRuntimeParameters mRTXDIShaderParams
-std::unique_ptr<rtxdi::Context> mpRTXDIContext
-uint mFrameIndex
-uint2 mFrameDim
-uint32_t mLastFrameReservoirID
-uint32_t mCurrentSurfaceBufferIndex
-CameraData mPrevCameraData
-mLights: Light
-mFlags: Flag
-mpPixelDebug: PixelDebug::SharedPtr
-mpAnalyticLightIDBuffer: Buffer::SharedPtr
-mpLightInfoBuffer: Buffer::SharedPtr
-mpLocalLightPdfTexture: Texture::SharedPtr
-mpEnvLightLuminanceTexture: Texture::SharedPtr
-mpEnvLightPdfTexture: Texture::SharedPtr
-mpLightTileBuffer: Buffer::SharedPtr
-mpCompactLightInfoBuffer: Buffer::SharedPtr
-mpReservoirBuffer: Buffer::SharedPtr
-mpSurfaceDataBuffer: Buffer::SharedPtr
-mpNeighborOffsetsBuffer: Buffer::SharedPtr
-mpReflectTypes: ComputePass::SharedPtr
-mpUpdateLightsPass: ComputePass::SharedPtr
-mpUpdateEnvLightPass: ComputePass::SharedPtr
-mpPresampleLocalLightsPass: ComputePass::SharedPtr
-mpPresampleEnvLightPass: ComputePass::SharedPtr
-mpGenerateCandidatesPass: ComputePass::SharedPtr
-mpTestCandidateVisibilityPass: ComputePass::SharedPtr
-mpSpatialResamplingPass: ComputePass::SharedPtr
-mpTemporalResamplingPass: ComputePass::SharedPtr
-mpSpatiotemporalResamplingPass: ComputePass::SharedPtr
-setShaderDataInternal(const ShaderVar&, const Texture::SharedPtr&);
-updateLights(RenderContext*);
-updateEnvLight(RenderContext*);
-presampleLights(RenderContext*);
-generateCandidates(RenderContext*, uint32_t);
-testCandidateVisibility(RenderContext*, uint32_t);
-uint32_t spatialResampling(RenderContext*, uint32_t);
-uint32_t temporalResampling(RenderContext*, const Texture::SharedPtr&, uint32_t, uint32_t)
-uint32_t spatiotemporalResampling(RenderContext*, const Texture::SharedPtr&, uint32_t, uint32_t)
-loadShaders()
-prepareResources(RenderContext*)
-setRTXDIFrameParameters()
}
@enduml