SPH Visualization through Marching Cubes (12 DEC 2021)
Marching Cubes in CUDA Sample Code
Algorithms:
1. Calculate number of vertices needed per voxel
2. Scan voxel occupied array to skip empty voxels
3. Compact voxel index array
4. Scan voxel vertex count array to read back total number of vertices
5. Generate triangles
Initial Variables
// Main.cpp
uint3 GridSizeLog2 = make_uint3(6u, 6u, 6u); // 6u, 6u, 6u
uint3 GridSizeShift = make_uint3(0u, GridSizeLog2.x, GridSizeLog2.x + GridSizeLog2.y); // 0u, 6u, 12u
uint3 GridSize = make_uint3(1u << GridSizeLog2.x, 1u << GridSizeLog2.y, 1u << GridSizeLog2.z); // 64u, 64u, 64u
uint3 GridSizeMask = make_uint3(GridSize.x - 1u, GridSize.y - 1u, GridSize.z - 1u); // 63u, 63u, 63u
float3 VoxelSize = make_float3(2.0f / static_cast<float>(GridSize.x),
2.0f / static_cast<float>(GridSize.y),
2.0f / static_cast<float>(GridSize.z)); // 0.03125f, 0.03125f, 0.03125f
uint NumVoxels = GridSize.x * GridSize.y * GridSize.z; // 262_144u
uint NumMaxVertices = GridSize.x * GridSize.y * 100u; // 409_600u
uint NumActiveVoxels = 0u;
uint NumTotalVertices = 0u;
float IsoValue = 0.2f;
float DeviceIsoValue = 0.005f;
// Device Data
GLuint PositionsVbo;
// CreateVbo(&PositionsVbo, NumMaxVertices * sizeof(float) * 4u);
GLuint NormalsVbo;
// CreateVbo(&NormalsVbo, NumMaxVertices * sizeof(float) * 4u);
struct cudaGraphicsResource* CudaPositionsVboResource;
// checkCudaErrors(CudaGraphicsGlRegisterBuffer(&CudaPositionsVboResource, PositionsVbo, cudaGraphicsMapFlagsWriteDiscard));
struct cudaGraphicsResource* CudaNormalsVboResource;
// checkCudaErrors(CudaGraphicsGlRegisterBuffer(&CudaNormalsVboResource, NormalsVbo, cudaGraphicsMapFlagsWriteDiscard));
float4* DevicePositions = nullptr;
// cudaMalloc(reinterpret_cast<void**>(&DevicePositions), NumMaxVertices * sizeof(float) * 4u);
float4* DeviceNormals = nullptr;
// cudaMalloc(reinterpret_cast<void**>(&DeviceNormals), NumMaxVertices * sizeof(float) * 4u);
uchar* DeviceVolumes = nullptr;
uint* DeviceVoxelVertices = nullptr;
uint* DeviceScannedVoxelVertices = nullptr;
uint* DeviceIsVoxelOccupied = nullptr;
uint* DeviceIsVoxelOccupiedScanned = nullptr;
uint* DeviceCompactVoxelArray = nullptr;
// uint MemorySize = sizeof(uint) * NumVoxels;
// checkCudaErrors(cudaMalloc(reinterpret_cast<void**>(&DeviceVoxelVertices), MemorySize));
// checkCudaErrors(cudaMalloc(reinterpret_cast<void**>(&DeviceScannedVoxelVertices), MemorySize));
// checkCudaErrors(cudaMalloc(reinterpret_cast<void**>(&DeviceIsVoxelOccupied), MemorySize));
// checkCudaErrors(cudaMalloc(reinterpret_cast<void**>(&DeviceIsVoxelOccupiedScanned), MemorySize));
// checkCudaErrors(cudaMalloc(reinterpret_cast<void**>(&DeviceCompactVoxelArray), MemorySize));
// tables
uint* DeviceNumVerticesTable = nullptr;
uint* DeviceEdgeTable = nullptr;
uint* DeviceTriTable = nullptr;
// AllocateTextures(&DeviceEdgeTable, &DeviceTriTable, &DeviceNumVerticesTable);
// MarchingCubesKernel.cu
// textures containing look-up tables
cudaTextureObject_t gTriTexture;
cudaTextureObject_t gNumVerticesTexture;
// volume data
cudaTextureObject_t gVolumesTexture;
1. Calculate number of vertices needed per voxel
void ClassifyVoxels(dim3 Grid,
dim3 Threads,
uint* OutVoxelVertices,
uint* OutIsVoxelOccupied,
uint3 GridSize,
uint3 GridSizeShift,
uint3 GridSizeMask,
uint NumVoxels,
float3 VoxelSize,
float IsoValue);
This function classifies voxels based on number of vertices it will generate. Each thread deals with a single voxel.
// Main.cpp
uint Threads = 128u;
dim3 Grid(NumVoxels / Threads, 1u, 1u); // 2_048u, 1u, 1u
// MarchingCubesKernel.cu
void ClassifyVoxels(dim3 Grid,
dim3 Threads,
uint* OutVoxelVertices,
uint* OutIsVoxelOccupied,
uint3 GridSize,
uint3 GridSizeShift,
uint3 GridSizeMask,
uint NumVoxels,
float3 VoxelSize,
float IsoValue
float4* SortedPositions,
uint* CellStarts,
uint* CellEnds)
{
ClassifyVoxelsDevice<<<Grid, Threads>>>(OutVoxelVertices,
OutIsVoxelOccupied,
GridSize,
GridSizeShift,
GridSizeMask,
NumVoxels,
VoxelSize,
IsoValue,
gNumVerticesTexture,
gVolumesTexture,
SortedPositions,
CellStarts,
CellEnds);
}
__global__
void ClassifyVoxelsDevice(uint* OutVoxelVertices,
uint* OutIsVoxelOccupied,
uint3 GridSize,
uint3 GridSizeShift,
uint3 GridSizeMask,
uint NumVoxels,
float3 VoxelSize,
float IsoValue,
cudaTextureObject_t gNumVerticesTexture,
cudaTextureObject_t gVolumesTexture,
float4* SortedPositions,
uint* CellStarts,
uint* CellEnds)
{
// threadIdx = 0u <= threadIdx.x < 128 (Threads), 0u, 0u
// blockIdx = 0u <= blockIdx.x < 2_048 (Grid.x), 0u, 0u
// gridDim = 2_048 (Grid.x), 0u, 0u
uint BlockIndex = blockIdx.y * gridDim.x + blockIdx.x;
uint Index = BlockIndex * blockDim.x + ThreadIdx.x;
uint3 GridPosition = CalculateGridPosition(Index, GridSizeShift, GridSizeMask);
float3 Position = make_float3(-1.0f + (GridPosition.x * VoxelSize.x),
-1.0f + (GridPosition.y * VoxelSize.y),
-1.0f + (GridPosition.z * VoxelSize.z));
// Read field values at neighbouring grid vertices
float Field[8] = { FLT_MAX, FLT_MAX, FLT_MAX, FLT_MAX,
FLT_MAX, FLT_MAX, FLT_MAX, FLT_MAX };
for (int z = -1; z <= 1; ++z)
{
for (int y = -1; y <= 1; ++y)
{
for (int x = -1; x <= 1; ++x)
{
int3 NeighborPosition = make_int3(GridPosition) + make_int3(x, y, z);
ClassifyVoxelByGrid(NeighborPosition,
Field,
Position,
SortedPositions,
VoxelSize,
CellStarts,
CellEnds);
}
}
}
// Calculate flag indicating if each vertex is inside or outside isosurface
uint CubeIndex;
CubeIndex = uint(Field[0] < IsoValue);
CubeIndex += uint(Field[1] < IsoValue) * 2u;
CubeIndex += uint(Field[2] < IsoValue) * 4u;
CubeIndex += uint(Field[3] < IsoValue) * 8u;
CubeIndex += uint(Field[4] < IsoValue) * 16u;
CubeIndex += uint(Field[5] < IsoValue) * 32u;
CubeIndex += uint(Field[6] < IsoValue) * 64u;
CubeIndex += uint(Field[7] < IsoValue) * 128u;
// Read number of vertices from texture
uint NumVertices = tex1Dfetch<uint>(gNumVerticesTexture, CubeIndex);
if (Index < NumVoxels)
{
OutVoxelVertices[Index] = NumVertices;
OutIsVoxelOccupied[Index] = (NumVertices > 0u);
}
}
__device__
void ClassifyVoxelsByGrid(int3 GridPosition,
float* OutField,
float3 Position,
float4* SortedPositions,
float3 VoxelSize,
uint* CellStarts,
uint* CellEnds)
{
uint GridHash = CalculateGridHash(GridPosition);
uint StartIndex = CellStarts[GridHash];
if (StartIndex != 0xffffffff)
{
uint EndIndex = CellEnds[GridHash];
for (uint NeighborIdx = StartIndex; NeighborIdx < EndIndex; ++NeighborIdx)
{
float3 NeighborPosition = make_float3(SortedPosition[i]);
float3 Rij = Position - NeighborPosition;
float R2 = Dot(Rij, Rij);
OutField[0] = Min(ScalarFieldFunction(Position, NeighborPosition), OutField[0]);
OutField[1] = Min(ScalarFieldFunction(Position + make_float3(VoxelSize.x, 0.0f, 0.0f), NeighborPosition), OutField[1]);
OutField[2] = Min(ScalarFieldFunction(Position + make_float3(VoxelSize.x, VoxelSize.y, 0.0f), NeighborPosition), OutField[2]);
OutField[3] = Min(ScalarFieldFunction(Position + make_float3(0.0f, VoxelSize.y, 0.0f), NeighborPosition), OutField[3]);
OutField[4] = Min(ScalarFieldFunction(Position + make_float3(0.0f, 0.0f, VoxelSize.z), NeighborPosition), OutField[4]);
OutField[5] = Min(ScalarFieldFunction(Position + make_float3(VoxelSize.x, 0.0f, VoxelSize.z), NeighborPosition), OutField[5]);
OutField[6] = Min(ScalarFieldFunction(Position + make_float3(VoxelSize.x, VoxelSize.y, VoxelSize.z), NeighborPosition), OutField[6]);
OutField[7] = Min(ScalarFieldFunction(Position + make_float3(0.0f, VoxelSize.y, VoxelSize.z), NeighborPosition), OutField[7]);
}
}
}
__device__
float ScalarFieldFunction(float3 Position, float3 NeighborPosition)
{
return LengthSquard(Position - NeighborPosition) - gParameters.KernelRadiusSquared;
}
First of all, we need to define the field function to determine the grid’s current status. In this source code, I have defined the field value to be the minimum squared distance between the particles in the adjacent grids. Afterwards, based on these scalar values in each corners, we can determine the number of vertices needed in each grids using predefined table, gNumVerticesTexture. For example, if the cube index is 0b1001 1001, which is depicted in the figure below:
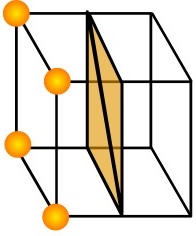
2. Scan occupied voxel array to skip empty voxels
We need two meshes, thus we need total 6 vertices. We save this value into OutVoxelVertices, and we can use this value to tell whether the grid is occupied with some vertices or not, and save it into OutIsVoxelOccupied. The reason we need OutIsVoxelOccupied is to add up all the values in this array to get the total number of voxels that actually contain vertices.
// Main.cpp
// scan voxel occupied array
ThrustScanWrapper(DeviceIsVoxelOccupiedScanned, DeviceIsVoxelOccupied, NumVoxels);
// MarchingCubesKernel.cu
void ThrustScanWrapper(uint* Output, uint* Input, uint NumElements)
{
thrust::exclusive_scan(thrust::device_ptr<unsigned int>(Input),
thrust::device_ptr<unsigned int>(Input + NumElements),
thrust::device_ptr<unsigned int>(Output));
}
For example, if DeviceIsVoxelOccupied is { 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1 }, then the output DeviceIsVoxelOccupiedScanned will be { 0, 0, 0, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3 }. Thus, if we add the last element of the DeviceIsVoxelOccupied and the last element of DeviceIsVoxelOccupiedScanned, we can get the total number of vertices actually needed.
uint LastElement;
uint LastScannedElement;
checkCudaErrors(cudaMemcpy(reinterpret_cast<void*>(&LastElement),
reinterpret_cast<void*>(DeviceIsVoxelOccupied + NumVoxels - 1u),
sizeof(uint),
cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost));
checkCudaErrors(cudaMemcpy(reinterpret_cast<void*>(&LastScannedElement),
reinterpret_cast<void*>(DeviceIsVoxelOccupiedScanned + NumVoxels - 1u),
sizeof(uint),
cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost));
NumActivelVoxels = LastElement + LastScannedElement;
Using the value of NumActivelVoxels, we can stop the process when the number of voxels with vertices is 0, which basically means that there is no meshes to render.
Now we continue to compact voxel index array.
3. Compact voxel index array
void GetCompactedVoxels(dim3 Grid, dim3 Threads, uint* OutCompactedVoxelArray, uint* IsVoxelOccupied, uint* IsVoxelOccupiedScanned, uint NumVoxels)
{
GetCompactedVoxelsDevice<<<Grid, Threads>>>(OutCompactedVoxelArray,
IsVoxelOccupied,
IsVoxelOccupiedScanned,
NumVoxels);
getLastCudaError("GetCompactedVoxelsDevice failed");
}
__global__
void GetCompactedVoxelsDevice(uint* OutCompactedVoxelArray, uint* IsVoxelOccupied, uint* IsVoxelOccupiedScanned, uint NumVoxels)
{
uint BlockIndex = blockIdx.y * gridDim.x + blockIdx.x;
uint Index = BlockIndex * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
if (IsVoxelOccupied[Index] && (Index < NumVoxels))
{
OutCompactedVoxelArray[IsVoxelOccupiedScanned[Index]] = Index;
}
}
The code itself is very short and straightforward. For example, using the example used previously, we know that IsVoxelOccupied is { 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1 } and IsVoxelOccupiedScanned is { 0, 0, 0, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3 }. Using this input,
IsVoxelOccupied[2]is1and2is less thanNumVoxels,OutCompactedVoxelArray[IsVoxelOccupiedScanned[2]]is equal toOutCompactedVoxelArray[0], which is assigned with a value of2IsVoxelOccupied[3]is1and3is less thanNumVoxels,OutCompactedVoxelArray[IsVoxelOccupiedScanned[3]]is equal toOutCompactedVoxelArray[1], which is assigned with a value of3IsVoxelOccupied[5]is1and5is less thanNumVoxels,OutCompactedVoxelArray[IsVoxelOccupiedScanned[5]]is equal toOutCompactedVoxelArray[2], which is assigned with a value of5IsVoxelOccupied[7]is1and7is less thanNumVoxels,OutCompactedVoxelArray[IsVoxelOccupiedScanned[7]]is equal toOutCompactedVoxelArray[3], which is assigned with a value of7
Now, we can see that CompatedVoxelArray is { 2, 3, 5, 7 }. These indices represents the indices of IsVoxelOccupied that contains 1. We can see that IsVoxelOccupied[2] == IsVoxelOccupied[3] == IsVoxelOccupied[5] == IsVoxelOccupied[7] == 1 while the other elements are all 0.
4. Scan voxel vertex count array to read back total number of vertices
// Main.cpp
ThrustScanWrapper(DeviceScannedVoxelVertices, DeviceVoxelVertices, NumVoxels);
If DeviceVoxelVertices was { 0, 0, 6, 3, 0, 6, 0, 9 }, then DeviceScannedVoxelVertices becomes { 0, 0, 0, 6, 9, 9, 15, 15 }. By adding the last elements of each array, we can get the total number of vertices required.
5. Generate triangles
#define NTHREADS (32)
void GenerateTriangles(dim3 Grid,
dim3 Threads,
float4* OutPositions,
float4* OutNormals,
uint* CompactedVoxelArray,
uint* NumVerticesScanned,
uint3 GridSize,
uint3 GridSizeShift,
uint3 GridSizeMask,
float3 VoxelSize,
float IsoValue,
uint NumActivelVoxels,
uint NumMaxVertices)
{
GenerateTrianglesDevice<<<Grid, NTHREADS>>>(OutPositions,
OutNormals,
CompactedVoxelArray,
NumVerticesScanned,
GridSize,
GridSizeShift,
GridSizeMask,
VoxelSize,
IsoValue,
NumActiveVoxels,
NumMaxVertices,
gTriTexture,
gNumVerticesTexture);
getLastCudaError("GenerateTrianglesDevice failed");
}
// generate triangles for each voxel using marching cubes
// interpolates normals from field function
__global__
void GenerateTrianglesDevice(float4* OutPositions,
float4* OutNormals,
uint* CompactedVoxelArray,
uint* NumVerticesScanned,
uint3 GridSize,
uint3 GridSizeShift,
uint3 GridSizeMask,
float3 VoxelSize,
float IsoValue,
uint NumActivelVoxels,
uint NumMaxVertices,
cudaTextureObject_t TriTexture,
cudaTextureObject_t NumVerticesTexture)
{
uint BlockIndex = blockIdx.y * gridDim.x + blockIdx.x;
uint Index = BlockIndex * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
if (Index > NumActiveVoxels - 1;)
{
// can't return here because of syncthreads()
Index = NumActiveVoxels - 1u;
}
uint VoxelIndex = CompactedVoxelArray[Index];
// Compute position in 3d grid
uint3 GridPosition = CalculateGridPosition(VoxelIndex, GridSizeShift, GridSizeMask);
float3 Position = make_float3(-1.0f + (static_cast<float>(GridPosition.x) * VoxelSize.x),
-1.0f + (static_cast<float>(GridPosition.y) * VoxelSize.y),
-1.0f + (static_cast<float>(GridPosition.z) * VoxelSize.z));
// Calculate cell vertex position
float3 Vertices[8] = { Position,
Position + make_float3(VoxelSize.x, 0.0f, 0.0f),
Position + make_float3(VoxelSize.x, VoxelSize.y, 0.0f),
Position + make_float3(0.0f, VoxelSize.y, 0.0f),
Position + make_float3(0.0f, 0.0f, VoxelSize.z),
Position + make_float3(VoxelSize.x, 0.0f, VoxelSize.z),
Position + make_float3(VoxelSize.x, VoxelSize.y, VoxelSize.z),
Position + make_float3(0.0f, VoxelSize.y, VoxelSize.z) };
float4 Field[8] = { make_float4(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, FLT_MAX),
make_float4(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, FLT_MAX),
make_float4(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, FLT_MAX),
make_float4(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, FLT_MAX),
make_float4(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, FLT_MAX),
make_float4(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, FLT_MAX),
make_float4(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, FLT_MAX),
make_float4(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, FLT_MAX) };
for (int z = -1; z <= 1; ++z)
{
for (int y = -1; y <= 1; ++y)
{
for (int x = -1; x <= 1; ++x)
{
int3 NeighborPosition = make_int3(GridPosition) + make_int3(x, y, z);
GenerateTrianglesByGrid(NeighborPosition,
Field,
Vertices,
SortedPositions,
VoxelSize,
CellStarts,
CellEnds);
}
}
}
// Recalculate flag
// (this is faster than storing it in global memory)
uint CubeIndex;
CubeIndex = uint(Field[0].w < IsoValue);
CubeIndex += uint(Field[1].w < IsoValue) << 1u;
CubeIndex += uint(Field[2].w < IsoValue) << 2u;
CubeIndex += uint(Field[3].w < IsoValue) << 3u;
CubeIndex += uint(Field[4].w < IsoValue) << 4u;
CubeIndex += uint(Field[5].w < IsoValue) << 5u;
CubeIndex += uint(Field[6].w < IsoValue) << 6u;
CubeIndex += uint(Field[7].w < IsoValue) << 7u;
// Find the vertices where the surface intersects the cube
// Use partitioned shared memory to avoid using local memory
__shared__ float3 VerticesList[12 * NTHREADS];
__shared__ float3 NormalsList[12 * NTHREADS];
LerpVertex(IsoValue, Vertices[0], Vertices[1], Field[0], Field[1], VerticesList[threadIdx.x], NormalsList[threadIdx.x]);
LerpVertex(IsoValue, Vertices[1], Vertices[2], Field[1], Field[2], VerticesList[threadIdx.x + NTHREADS], NormalsList[threadIdx.x + NTHREADS]);
LerpVertex(IsoValue, Vertices[2], Vertices[3], Field[2], Field[3], VerticesList[threadIdx.x + (NTHREADS * 2)], NormalsList[threadIx.x + (NTHREADS * 2)]);
LerpVertex(IsoValue, Vertices[3], Vertices[4], Field[3], Field[4], VerticesList[threadIdx.x + (NTHREADS * 3)], NormalsList[threadIx.x + (NTHREADS * 3)]);
LerpVertex(IsoValue, Vertices[4], Vertices[5], Field[4], Field[5], VerticesList[threadIdx.x + (NTHREADS * 4)], NormalsList[threadIx.x + (NTHREADS * 4)]);
LerpVertex(IsoValue, Vertices[5], Vertices[6], Field[5], Field[6], VerticesList[threadIdx.x + (NTHREADS * 5)], NormalsList[threadIx.x + (NTHREADS * 5)]);
LerpVertex(IsoValue, Vertices[6], Vertices[7], Field[6], Field[7], VerticesList[threadIdx.x + (NTHREADS * 6)], NormalsList[threadIx.x + (NTHREADS * 6)]);
LerpVertex(IsoValue, Vertices[7], Vertices[4], Field[7], Field[4], VerticesList[threadIdx.x + (NTHREADS * 7)], NormalsList[threadIx.x + (NTHREADS * 7)]);
LerpVertex(IsoValue, Vertices[0], Vertices[4], Field[0], Field[4], VerticesList[threadIdx.x + (NTHREADS * 8)], NormalsList[threadIx.x + (NTHREADS * 8)]);
LerpVertex(IsoValue, Vertices[1], Vertices[5], Field[1], Field[5], VerticesList[threadIdx.x + (NTHREADS * 9)], NormalsList[threadIx.x + (NTHREADS * 9)]);
LerpVertex(IsoValue, Vertices[2], Vertices[6], Field[2], Field[6], VerticesList[threadIdx.x + (NTHREADS * 10)], NormalsList[threadIx.x + (NTHREADS * 10)]);
LerpVertex(IsoValue, Vertices[3], Vertices[7], Field[3], Field[7], VerticesList[threadIdx.x + (NTHREADS * 11)], NormalsList[threadIx.x + (NTHREADS * 11)]);
__syncthreads();
// Output triangle vertices
uint NumVertices = tex1Dfetch<uint>(NumVerticesTexture, CubeIndex);
for (uint VertexIdx = 0u; VertexIdx < NumVertices; ++VertexIdx)
{
uint Edge = tex1Dfetch<uint>(TriTexture, CubeIndex * 16 + VertexIdx);
uint OriginalIndex = NumVerticesScanned[VoxelIndex] + VertexIdx;
if (OriginalIndex < NumMaxVertices)
{
OutPositions = make_float4(VerticesList[(Edge * NTHREADS) + threadIdx.x], 1.0f);
OutNormals = make_float4(NormalsList[(Edge * NTHREADS) + threadIdx.x], 0.0f);
}
}
}
__device__
void GenerateTrianglesByGrid(int3 GridPosition,
float4* OutField,
float3* Vertices,
float3 VoxelSize,
float4* SortedPositions,
uint* CellStarts,
uint* CellEnds)
{
uint GridHash = CalculateGridHash(GridPosition);
uint StartIndex = CellStarts[GridHash];
if (StartIndex != 0xffffffff)
{
uint EndIndex = CellEnds[GridHash];
for (uint NeighborIdx = StartIndex; NeighborIdx < EndIndex; ++NeighborIdx)
{
float3 NeighborPosition = make_float3(SortedPositions[NeighborIdx]);
for (uint VertexIdx = 0u; VertexIdx < 8u; ++VertexIdx)
{
float4 Gradient = VectorFieldFunction(Vertices[VertexIdx], NeighborPosition);
if (OutField[VertexIdx].w > Gradient.w)
{
OutField[VertexIdx] = Gradient;
}
}
}
}
}
__device__
float4 VectorFieldFunction(float3 Position, float3 NeighborPosition)
{
float ScalarValue = ScalarFieldFunction(Position, NeighborPosition);
const float Delta = 0.001f;
float DeltaX = ScalarFieldFunction(Position + make_float3(Delta, 0.0f, 0.0f), NeighborPosition) - ScalarValue;
float DeltaY = ScalarFieldFunction(Position + make_float3(0.0f, Delta, 0.0f), NeighborPosition) - ScalarValue;
float DeltaZ = ScalarFieldFunction(Position + make_float3(0.0f, 0.0f, Delta), NeighborPosition) - ScalarValue;
return make_float4(DeltaX, DeltaY, DeltaZ, ScalarValue);
}
// Compute interpolated vertex position and normal along an edge
__device__
LerpVertex(float IsoLevel, float3 Position0, float3 Position1, float4 Field0, float4 Field1, float3& OutPosition, float3& OutNormal)
{
float Alpha = (IsoLevel - Field0.w) / (Field1.w - Field0.w);
Position = Lerp(Position0, Position1, Alpha);
Normal.x = Lerp(Field0.x, Field1.x, Alpha);
Normal.y = Lerp(Field0.y, Field1.y, Alpha);
Normal.z = Lerp(Field0.z, Field1.z, Alpha);
}